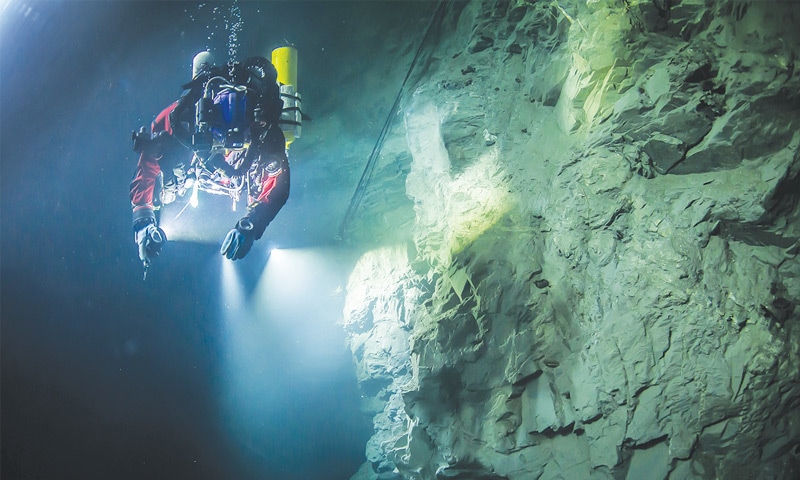
WARSAW: A team of explorers say they’ve discovered that a cave in the eastern Czech Republic is the world’s deepest flooded fissure, going at least 404 metres (1,325 feet) deep.
Polish explorer Krzysztof Starnawski, who led the team, said on Friday that he felt like a “Columbus of the 21th century” to have made the discovery near the Czech town of Hranice.
Starnawski, 48, determined on Tuesday that the flooded limestone Hranicka Propast, or Hranice Abyss, which divers, including him, have explored for decades in its upper parts, was at least 404 meters deep.
He scuba dived to a narrow slot in the rock formation at 200 meters down, then sent a remotely operated underwater robot, or ROV, that went to the depth of 404 meters, or the length of its cord, but still did not hit the bottom.
In 2015, Starnawski himself passed through the slot and went to 265 meters down without reaching the cave’s bottom, which made him want to do more exploring. But after diving that far down, Starnawski had to spend over six hours in a decompression chamber, and decided he needed a robot instead.
Speaking on the phone from his home in Krakow, southern Poland, Starnawski said Tuesday’s discovery makes Hranice Abyss the world’s deepest known underwater cavity, beating the previous record-holder, a flooded sinkhole in Italy called Pozzo del Merro, by 12 metres (39 feet).

The Czech Speleological Society said it thinks the cave is even deeper and will yield additional records. When the robot was 404 meters deep “it was as deep as its rope could go, but the bottom was still nowhere in sight,” the society said.
Diving in the cave is a challenge, because of its muddy areas and a water temperature of 15 degrees Celsius (59 degrees Fahrenheit).
The water’s mineral composition also damages equipment and injures exposed skin, Starnawski said. “But that is the only price to be paid for this discovery, and it was worth paying,” he said.
A cross-section map he made of the cave ends with question marks in an unexplored area where he believes the fissure goes deeper. On Saturday, he plans to dive to 200 meters again to bring the robot back through the narrow passage. The device was made especially for the expedition and operated by a Polish firm, GRALmarine.
Starnawski said National Geographic, which first reported the discovery , covered some of the expedition’s cost.
Published in Dawn, October 1st, 2016