The Bath Island area is a posh locality in Karachi. Luxury apartments with eye-watering price tags of Rs60m have mushroomed up in place of the regal old money bungalows. Adjacent to it is a katchi abadi, a source of emergency eggs and bread in the morning from the numerous kirayana stores that cater to the impoverished and wealthy alike.
Some of Pakistan’s most expensive urban areas have a katchi abadi attached to them. Slum areas are ubiquitous all over the country and provide a never-ending supply of maids that keep the sprawling bungalows spick and span.
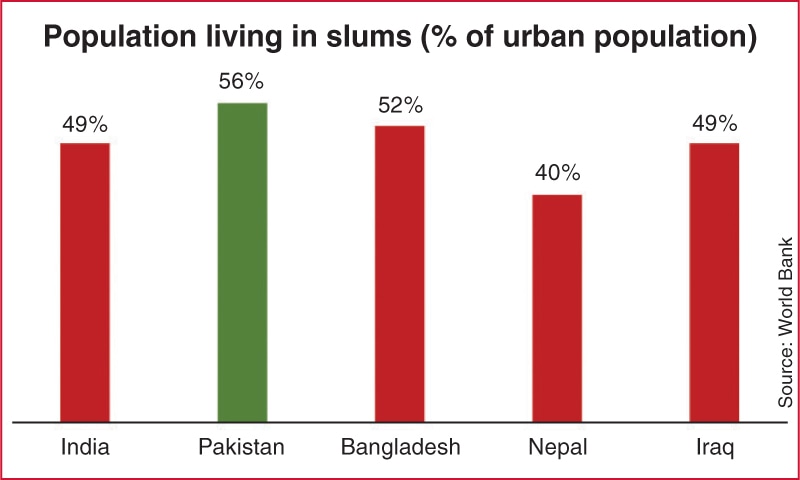
Among regional countries, Pakistan has the highest ratio of slums as a percentage of the total urban population. In Karachi and Hyderabad alone, there are around 1,300 slums, as per Unicef. One of which is Orangi Town, with the dubious distinction of being amongst the five biggest slums in the world. In 2016, an estimated 2.4m people lived there, more than the population of Paris.
Since these numbers are from before the recent super floods, so in all likelihood, the percentage has increased.
Slums exist because of rapid rural-to-urban migration and poverty. The lack of affordable housing pushes those at the lowest strata of society to move to low-cost and congested regions where homes are flimsily constructed. The abadis generally have high crime and death rates, pollution and incidence of alcohol and drug addiction, according to research by the Centre for Business and Society, LUMS.
In the best of times, when the economy is flourishing, the inhabitants do not have access to sanitation and clean drinking water. At the brink of a default, the country has little left to give to those at the bottom of the pyramid. Much of the informal economy, which employs over two-thirds of the labour force, resides in slum areas.
Katchi abadis are intergenerational poverty traps where most of life is spent trying to keep body and soul together. Recurrent diseases, few opportunities for education, a large number of children and low incomes of households prevent the upward movement of people residing in slums.
The higher incidence in Pakistan indicates that future generations will lag further behind their peers in regional countries. Bangladesh and India, neither of which are grappling with Pakistan’s political or economic climate, are already ahead in terms of development and stability.
Published in Dawn, The Business and Finance Weekly, March 27th, 2023














































Dear visitor, the comments section is undergoing an overhaul and will return soon.